IAOMT SMART Mercury Removal Protocol:
Mercury amalgam dental filings have been shown to shed mercury on a continual basis. Mercury is bio-accumulative and aggregates in fatty tissue including the brain and over time leading to toxic symptoms including Parkinson's disease. For more information on mercury, mercury detoxification and the pathology of mercury see the link between mercury and Parkinson's disease.
This chronic condition can only be halted by removing the amalgam fillings safely. A regular dentist who does not follow any safety protocol is more likely to stir up and intoxicate the patient with mercury particles and vapors. This has led to the development of the IAOMT SMART protocol for the safe removal of mercury amalgam dental filings. The International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology (IAOMT) Safe Mercury Amalgam Removal Technique (SMART) is shown in operation.
Shown below are photos of some of the tenants of the SMART protocol:- provide the patient and dental workers protective gowns
- provide the dental workers protective face shields, head coverings, non-latex nitrile gloves and mask
- the use of an evacuation system to remove mercury dust and vapors from the patient's mouth
- the use of an air supply so the patient does not breathe in mercury vapors
- the use of a dam around the teeth being worked on to trap debris from being ingested by the patient
- the use of amalgam capture separators to capture material so that it is not released into the public waste system or atmosphere
The IAOMT began SMART training (including online eLearning) and SMART certification for dentists in 2016. SMART certification will allow a dentist to be added to the IAOMT Dentist's Worldwide Directory.
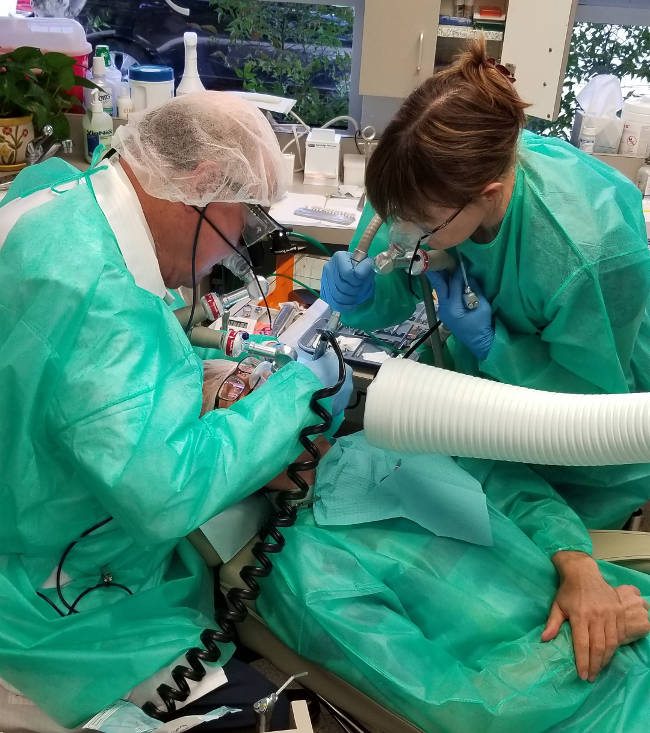
Dentist and dental patient and the use of the IAOMT SMART protocol. Dr McBride DDS

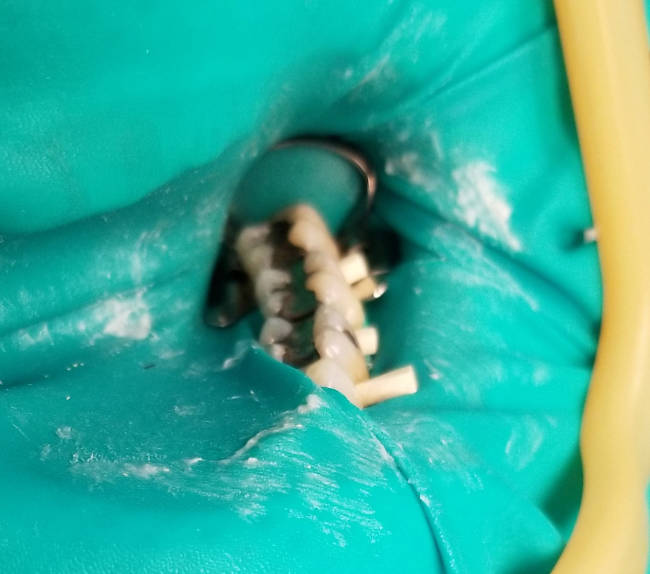
Dental dam blocks the ingestion of mercury and protects the patient from mercury exposure
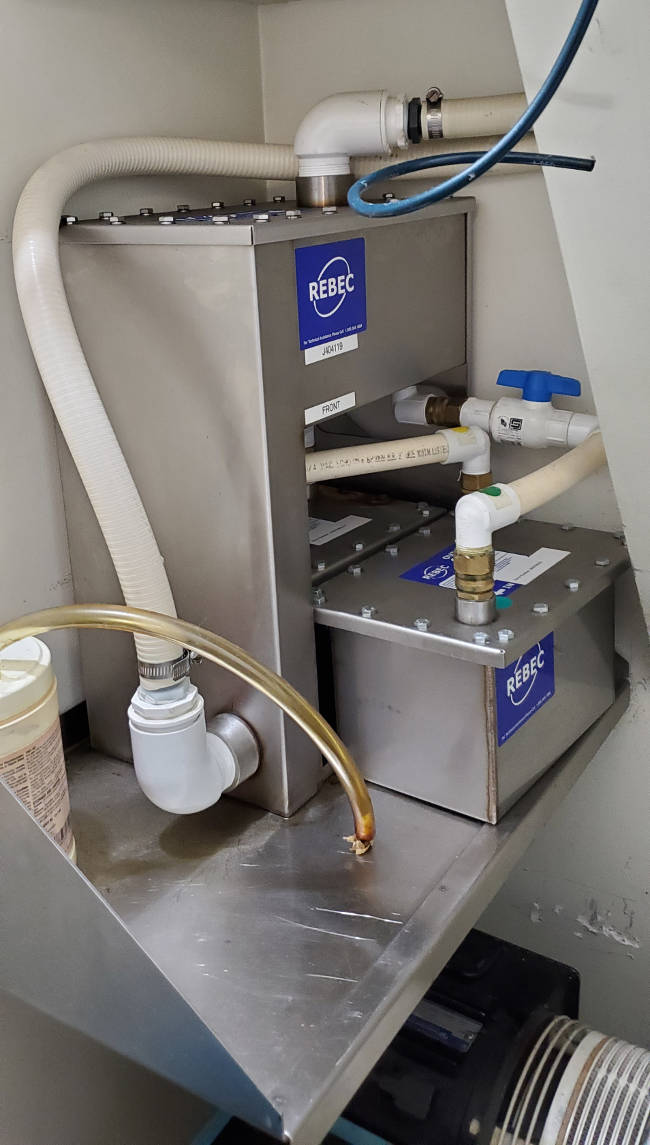

Mercury reclaimation from waste water is required before releasing water to the sewer system
Dental mercury amalgam replacement:
Shown below are photos of the transformation.
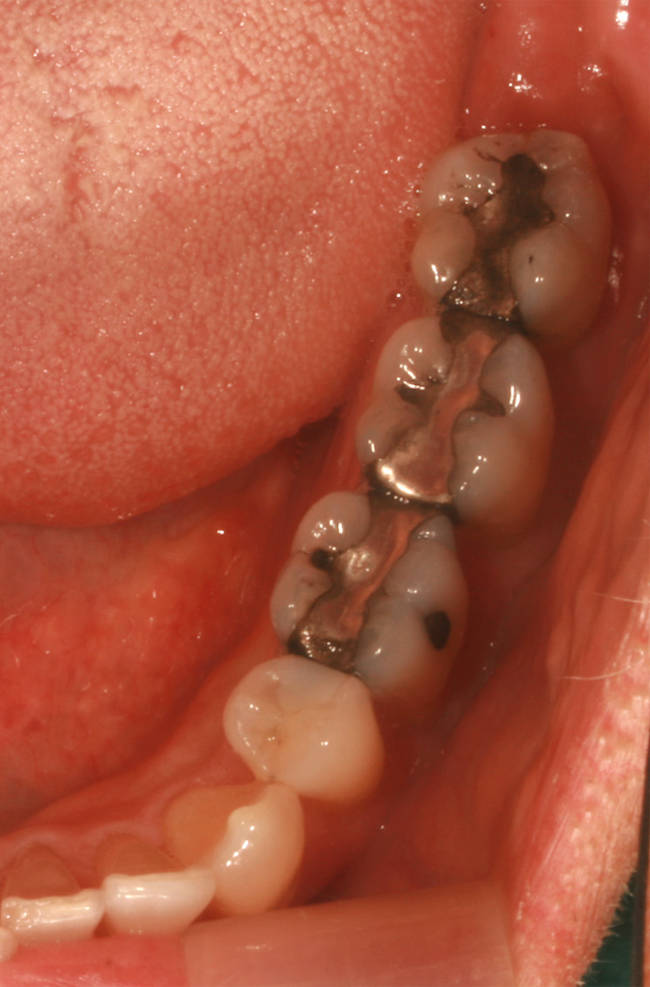
Lower quadrant with three teeth having mercury amalgam fillings
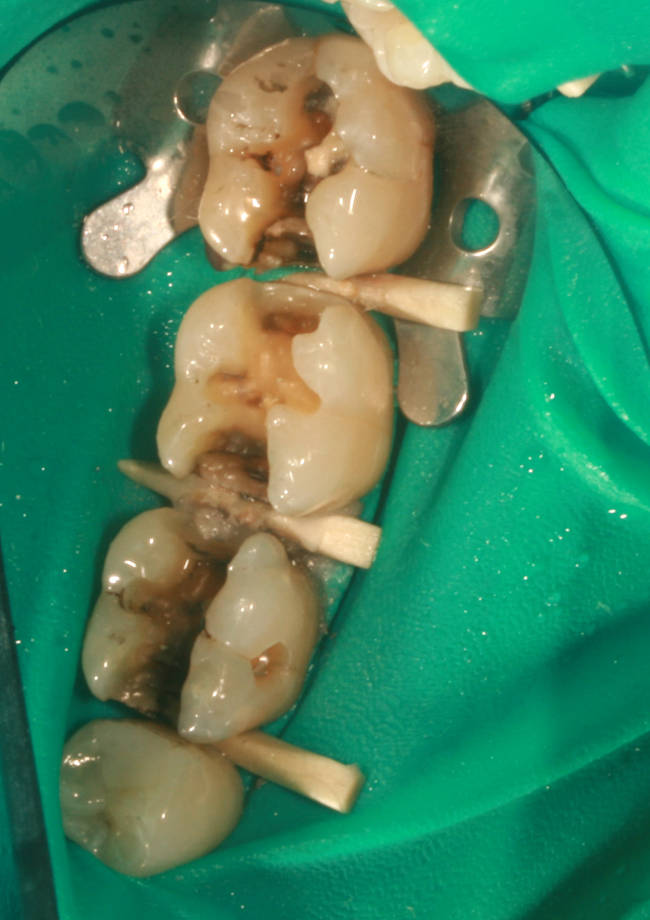
Mercury amalgam removed. Once removed one can readily see the extensive volume of mercury amalgam filling that was once present.
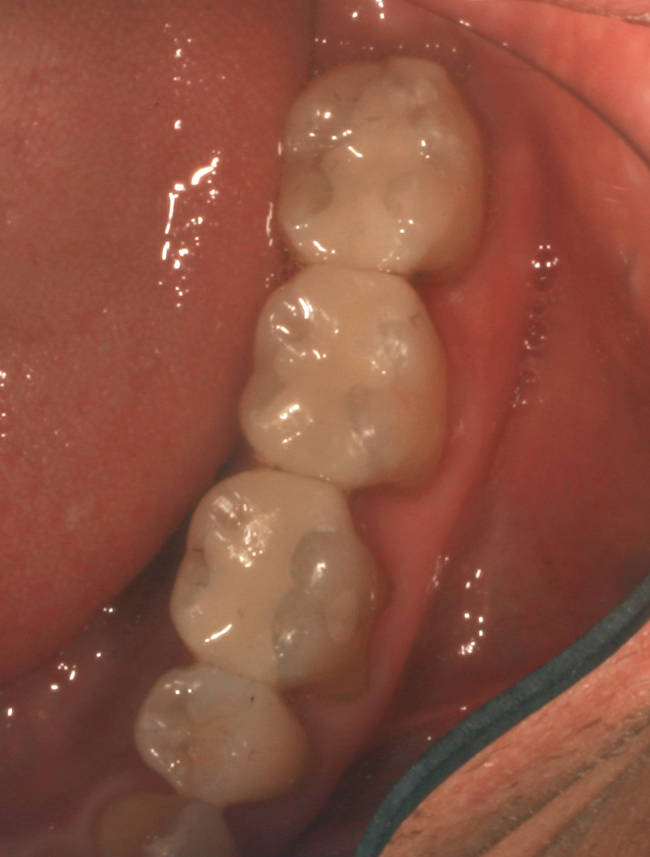
Lower quadrant with three teeth having ceramic fillings
Crowns:
Note that crowns can be problematic as there may be a lot of mercury amalgam under the crown and an X-ray will not be able to indicate one way or the other. Typically crowns have to be physically removed in order to inspect the conditions underneath. Removal is important to those who wish to undergo chelation therapy as the chelator may work its way from the blood supply in the root of the tooth to the amalgam if not removed and during this process the root of the tooth can be harmed requiring a root canal.
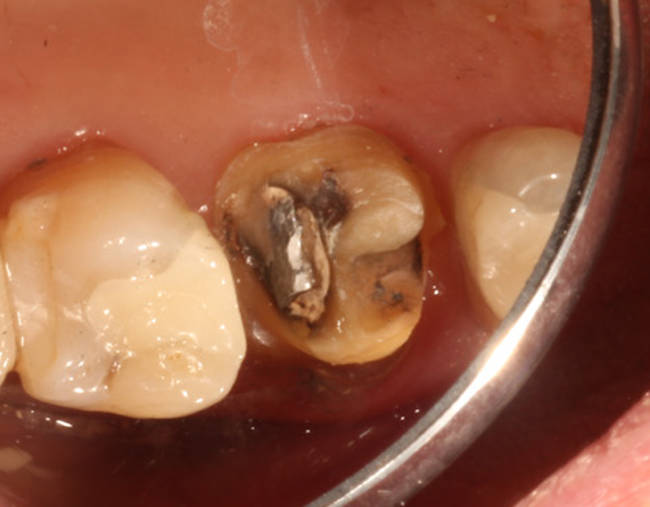
The amalgam found under a crown
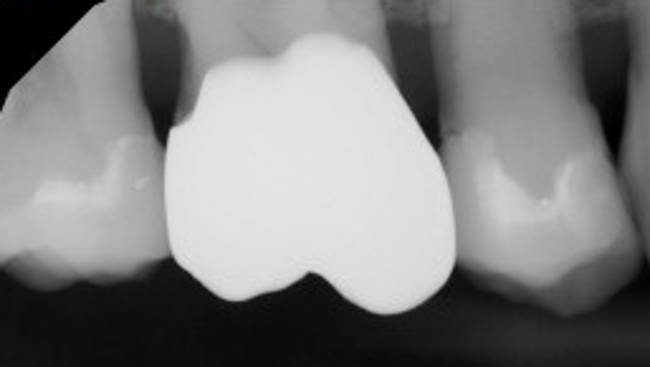
Crown hides what is under the crown from an X-ray
Mercury specs and reminants:
X-rays will reveal if the replacement work was sucessful. If not done properly, a spec of mercury amalgam may have been left behind. The spec shown below is shown near the root of the tooth. This is not acceptable if one is going to follow-up with chelation therapy as the chelator may work its way from the blood supply to the spec of mercury, damaging the root of the tooth and eventually requiring a root canal.
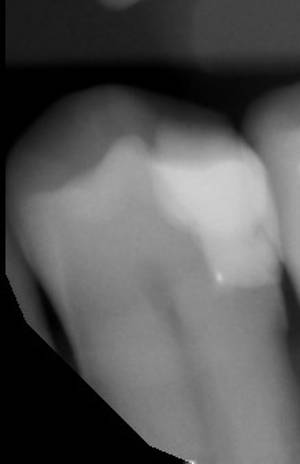
X-ray showing spec of amalgam near tooth root
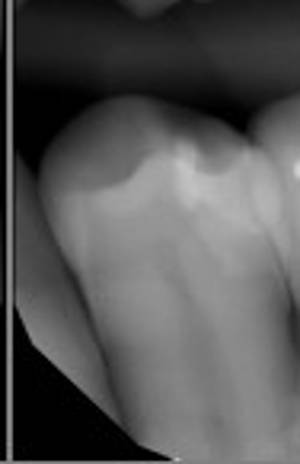
X-ray showing spec of amalgam removed
Binders:
A binder is a substance which binds to toxins for the journey through the Gastrointestinal (GI) tract so that the toxin does not get reabsorbed by the body. The function of the GI tract is absorption but this function must be mitigated in the case of mercury which could become available during the drilling and removal process. Typically binders consist of activated charcoal, bentonite clay or zeolite but those with a thiol group (containing sulfur) have been developed to specifically bond to mercury.
It is advised by the IAOMT to consume a binder before the amalgam removal procedure.
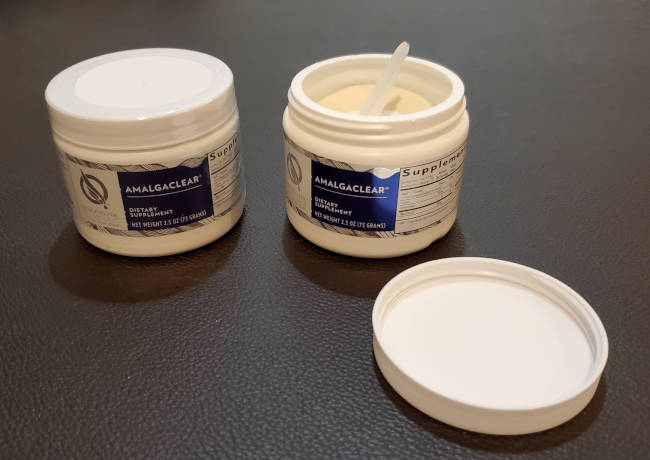

Quicksilver Scientific Amalgaclear:
- Vitamin C: antioxidant and free radical protection
- sodium
- thiol-functionalized silica (IMD): binds to mercury
- modified citrus pectin: binds to a variety of heavy metals
- acacia gum: enhances beneficial gut bacteria
Label: "Warning: This product can expose you to chemicals including lead, which is known to the State of California to cause birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to P65Warnings.ca.gov"
Really! Details please. No quantitative information given.
For more information on mercury, mercury detoxification and the pathology of mercury see the link between mercury and Parkinson's disease.
Pros:
- No negative side effects. Removal of neurotoxic mercury source will remove a bioaccumulative hazard and Parkinson's instigator.
Cons:
- Cost and increased effort to have mercury removed safely